Yunnan
| Yunnan Province | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Abbreviations: 滇 or 云 (pinyin: Diān or Yún) | |||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| Origin of name | 云 yún – Yunling Mountains 南 nán – south "South of the Yunling Mountains"[1] |
||||||||
| Administration type | Province | ||||||||
| Capital | Kunming | ||||||||
| Largest city | Kunming | ||||||||
| CPC Ctte Secretary | Bai Enpei | ||||||||
| Governor | Qin Guangrong | ||||||||
| Area | 394,100 km2 (152,200 sq mi) (8th) | ||||||||
| - Latitude | {{{Latitude}}} | ||||||||
| - Longitude | {{{Longitude}}} | ||||||||
| Population (2009) - Density |
45,710,000 (12th) 112 /km2 (290 /sq mi) (24th) |
||||||||
| GDP (2009) - per capita |
CNY 616.8 billion (24rd) CNY 13,494 (29th) |
||||||||
| HDI (2008) | 0.710 (medium) (28th) | ||||||||
| Ethnic composition | Han – 67% Yi – 11% Bai – 3.6% Hani – 3.4% Zhuang – 2.7% Dai – 2.7% Miao – 2.5% Hui – 1.5% Tibetan – 0.3% |
||||||||
| Prefecture-level | 16 divisions | ||||||||
| County-level | 129 divisions | ||||||||
| Township-level* | 1565 divisions | ||||||||
| ISO 3166-2 | CN-53 | ||||||||
| Official website http://www.yn.gov.cn (Simplified Chinese) |
|||||||||
| Source for population and GDP data:
《中国统计年鉴—2005》 China Statistical Yearbook 2005
Source for nationalities data:
ISBN 7503747382 《2000年人口普查中国民族人口资料》 Tabulation on nationalities of 2000 population census of China
*As at December 31, 2004ISBN 7105054255 |
|||||||||
| Template ■ Discussion ■ WikiProject China | |||||||||
Yunnan (simplified Chinese: 云南; traditional Chinese: 雲南; pinyin: Yúnnán, IPA: [y̌nnǎn] (![]() listen); literally "South of the Clouds") is a province of the People's Republic of China, located in the far southwest of the country spanning approximately 394,000 square kilometers (152,000 square miles). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders Burma, Laos, and Vietnam.
listen); literally "South of the Clouds") is a province of the People's Republic of China, located in the far southwest of the country spanning approximately 394,000 square kilometers (152,000 square miles). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders Burma, Laos, and Vietnam.
Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the northwest and low elevations in the southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the relative height from mountain peaks to river valleys can be as much as 3,000 m. Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of higher plants in China, Yunnan has over 17,000. Yunnan's reserves of aluminium, lead, zinc and tin are the largest in China, and there are also major reserves of copper and nickel. Yunnan has over 600 rivers and lakes, which provide an annual water supply of 222 billion cubic meters. Projected hydropower reserves stand at 103 GW, with an exploitable capacity of 90 GW.
Yunnan became part of the Han Dynasty (206 BC-220 AD) during 2nd century BC. It became the seat of a Tibeto-Burman speaking kingdom known as Nanzhao in the 8th century. Nanzhao was multi-ethnic, but the elite most likely spoke a northern dialect of Yi, which became established as the prestige dialect (see Nuosu language). The Mongols conquered the region in the 13th century, with local control exercised by warlords until the 1930s. As with other parts of China's southwest, Japanese occupation in the north during World War II forced a migration of Chinese into the region. Ethnic minorities in Yunnan account for about 34 percent of its total population. Major ethnic groups include Yi, Bai, Hani, Zhuang, Dai and Miao.
Contents |
Emblem
Camellia reticulata, a plant native to Yunnan Province, is the emblem of this province.
History
The Yuanmou Man, a Homo erectus fossil unearthed by railway engineers in the 1960s, has been determined to be the oldest known hominid fossil in China. By the Neolithic period, there were human settlements in the area of Lake Dian. These people used stone tools and constructed simple wooden structures.
Around the third century BC, the central area of Yunnan around present day Kunming was known as Dian. The Chu general Zhuang Qiao (庄跤) entered the region from the upper Yangtze River and set himself up as "King of Dian". He and his followers brought into Yunnan an influx of Chinese influence, the start of a long history of migration and cultural expansion.

In 221 BC, Qin Shi Huang unified China and extended his authority south. Commanderies and counties were established in Yunnan. An existing road in Sichuan – the "Five Foot Way" – was extended south to around present day Qujing (曲靖), in eastern Yunnan. In 109 BC, Emperor Wu sent General Guo Chang (郭昌) south to Yunnan, establishing Yizhou commandery and 24 subordinate counties. The commandery seat was at Dianchi county (present day Jinning 晋宁). Another county was called "Yunnan", probably the first use of the name. To expand the burgeoning trade with Burma and India, Emperor Wu also sent Tang Meng (唐蒙) to maintain and expand the Five Foot Way, renaming it "Southwest Barbarian Way" (西南夷道). By this time, agricultural technology in Yunnan had improved markedly. The local people used bronze tools, plows and kept a variety of livestock, including cattle, horses, sheep, goats, pigs and dogs. Anthropologists have determined that these people were related to the people now known as the Tai. They lived in tribal congregations, sometimes led by exiled Chinese.
During the Three Kingdoms, the territory of present day Yunnan, western Guizhou and southern Sichuan was collectively called Nanzhong. The dissolution of Chinese central authority led to increased autonomy for Yunnan and more power for the local tribal structures. In AD 225, the famed statesman Zhuge Liang led three columns into Yunnan to pacify the tribes. His seven captures of Meng Huo, a local magnate, is much celebrated in Chinese folklore.
In the fourth century, northern China was largely overrun by nomadic tribes from the north. In the 320s, the Cuan (爨) clan migrated into Yunnan. Cuan Chen (爨琛) named himself king and held authority from Lake Dian (then called Kunchuan [昆川]). Henceforth the Cuan clan ruled Yunnan for over four hundred years. In 738, the kingdom of Nanzhao was established in Yunnan by Piluoge (皮罗阁), who was confirmed by the imperial court of the Tang Dynasty as king of Yunnan. Ruling from Dali, the thirteen kings of Nanzhao ruled over more than two centuries and played a part in the dynamic relationship between China and Tibet. In 937, Duan Siping (段思平) overthrew the Nanzhao and established the Kingdom of Dali. The kingdom was conquered by the Mongol Empire in 1253. During the Yuan Dynasty Kublai Khan appointed the first governor, Turkmen Sayid Ajall, in Yunnan in 1273.[2] Before that, the area had been ruled by a local king and a Mongol prince under the Great Khan. Yunnan and Hunan were main bases for Mongol military operations in Indo-China. The Ming Dynasty destroyed the Yuan loyalists in 1381.
In 1894, George Ernest Morrison, an Australian correspondent for The Times, travelled from Beijing to British-occupied Burma via Yunnan. His book, An Australian in China,[3] details his experiences.
Yunnan was transformed enormously by the events of the war against Japan, which caused many east coast refugees and industrial establishments to relocate to the province. It assumed great strategic significance, particularly as the Burma Road was constructed from Kunming to Lashio in Burma during this time.
Naturalists
From 1916 to 1917, Roy Chapman Andrews and Yvette Borup Andrews led the Asiatic Zoological Expedition of the American Museum of Natural History through much of western and southern Yunnan, as well as other provinces of China. The book, Camps and Trails in China, records their experiences.
Other notable explorers include Heinrich Handel-Mazzetti, George Forrest (botanist), Joseph Francis Charles Rock who from 1922–1949 spent most of his time studying the flora, peoples and languages of southwest China, mainly in Yunnan, and Peter Goulart, a White Russian who studied Naxi culture and lived in Lijiang from 1940 to 1949.
Geography



Yunnan is the most southwestern province in China, with the Tropic of Cancer running through its southern part. The province has an area of 394,000 square km, 4.1% of the nation's total. The northern part of the province forms part of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. The province borders Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region and Guizhou Province in the east, Sichuan Province in the north, and Tibet Autonomous Region in the northwest. It shares a border of 4,060 km with Burma in the west, Laos in the south, and Vietnam in the southeast.
Climate
Yunnan has a generally mild climate with pleasant and fair weather because of the province's location on south-facing mountain slopes, receiving the influence of both the Pacific and Indian oceans, and although the growing period is long, there is little arable land. See Agriculture in Yunnan. January average temperatures range from 8°C to 17°C; July averages vary from 21°C to 27°C. Average annual rainfall ranges from 600 mm to 2,300 mm, with over half the rain occurring between June and August. The plateau region has moderate temperatures. The western canyon region is hot and humid at the valley bottoms, but there are freezing winds at the mountaintops.
Topography
The terrain is largely mountainous, especially in the north and west. A series of high mountain chains spreads across the province. There is a distinct canyon region to the west and a plateau region to the east. Yunnan's major rivers flow through the deep valleys between the mountains.
The average elevation is 1,980 m. The mountains are highest in the north where they reach more than 5,000 m; in the south they rise no higher than 3,000 m. The highest point in the north is the Kawagebo Peak in Deqin County on the Diqing Plateau, which is about 6,740 meters high; and the lowest is in the Honghe River Valley in Hekou County, with an elevation of 76.4 meters.
The eastern half of the province is a limestone plateau with karst scenery and unnavigable rivers flowing through deep mountain gorges; the western half is characterized by mountain ranges and rivers running north and south. These include the Nujiang (Thai: Salween) and the Lancangjiang (Thai: Mekong). The rugged, vertical terrain produces a wide range of flora and fauna, and the province has been called a natural zoological and botanical garden.
Borders
Bordering provinces are Tibet, Sichuan, Guizhou and Guangxi. Bordering countries are Vietnam (the main border crossing by road and rail is at Hekou–Lao Cai, the only land border crossing open to non-Chinese/non-Vietnamese), Laos (at Boten) and Burma (with the main border crossing at Ruili, the only land border open to non-Chinese/non-Burmese).
Lakes
There are several major lakes in Yunnan. The province has nine lakes with areas of over 30 square kilometers.[4] They include:
- Dianchi Lake, near Kunming
- Fuxian Lake, in Yuxi, the second deepest lake in China
- Erhai Lake, near Dali
- Lugu Lake, in Ninglang near the border with Sichuan
- Qilu Lake, directly south of Fuxian Lake and in Tonghai County
- Yangzong Lake, in Yiliang County, Kunming Prefecture
- Yilong Lake
- Xingyun Lake
Rivers
Yunnan is the source of two rivers, the Xi River (there known as the Nanpan and Hongshui) and the Yuan River. The Hongshui is a principal source stream of the Xi River. Rising as the Nanpan in eastern Yunnan province, it flows south and east to form part of the boundary between Guizhou province and Guangxi autonomous region. Flowing for 345 km, it unites with the Yu River at Guiping to form what eventually becomes the Xi River.
The province is drained by six major river systems:
- the Yangtze River, here known as the Jinsha Jiang (River of Golden Sands), drains the province's north.
- the Pearl River, with its source near Qujing, collects the waters from the east.
- the Mekong (Lancang), which flows from Tibet into the South China Sea forming the boundaries between Laos and Burma, between Laos and Thailand, through Cambodia and Vietnam
- the Red River (Yuan or Honghe) has its source in the mountains south of Dali and enters the South China Sea through Hanoi, Vietnam
- the Salween (Nujiang), which flows into the Gulf of Martaban and the Andaman Sea through Burma
- the Irrawaddy has a few small tributaries in Yunnan's far west, such as the Dulongjiang, and rivers in the prefecture of Dehong.
National parks
- Pudacuo National Park, opened in 2007, in Shangri-La County
- Laojunshan National Park (老君山国家公园), in Lijiang Prefecture, pending approval[5]
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
- Old Town of Lijiang, accepted in 1997 as a cultural site
- Three Parallel Rivers of Yunnan Protected Areas, accepted in 2003 as a natural site
- South China Karst, accepted in 2007 as a natural site [6]
Geology
The eastern half of the province is a limestone plateau with karst scenery and unnavigable rivers flowing through deep mountain gorges; the western half is characterized by mountain ranges and rivers running north and south. These include the Salween and the Mekong River. The rugged, vertical terrain produces a wide range of flora and fauna, and the province has been called a natural zoological and botanical garden.
Yunnan has vast mineral resources that are its chief source of wealth. It is China's leading tin producer and has large deposits of iron, coal, lead, copper, zinc, gold, mercury, silver, antimony, and sulfur.
Paleontology
- Yunnanozoon – Lower Cambrian possible chordate
- Jingshanosaurus – Early Jurassic dinosaur
Biodiversity
Yunnan is China's most diverse province, biologically as well as culturally. The province contains snow-capped mountains and true tropical environments, thus supporting an unusually full spectrum of species and vegetation types. During summer, the Great Plateau of Tibet acts as a barrier to monsoon winds, trapping moisture in the province. This gives the alpine flora in particular what one source has called a "lushness found nowhere else."
This topographic range combined with a tropical moisture sustains extremely high biodiversity and high degrees of endemism, probably the richest botanically in the world's temperate regions. Over 15,000 species of higher plants, of which perhaps 2,500 are endemic, can be found in the province. The fauna is nearly as diverse. Yunnan Province has less than 4% of the land of China, yet contains about half of China's birds and mammals.
Yunnan Snub-nosed Monkey, also known as the Black Snub-nosed Monkey, is an endangered species of primate in the Cercopithecidae family.
See also Distribution of orchid species
Designation
Yunnan has been designated a:
- "Center of Plant Diversity" (IUCN/WWF: Davis et al. 1995)
- "Global 200 List Priority Ecoregion" for biodiversity conservation (WWF: Olsen and Dinerstein 1998)
- "Endemic Bird Area" (Birdlife International: Bibby, C. et al. 1992) and
- "Global Biodiversity Hotspot," as a part of the Hengdu Mountain Ecosystem (Conservation International: Mittermeier and Mittermeier 1997)
Natural resources
Yunnan not only has more plant species of tropical, subtropical, temperate, and frozen zones than any other province in the country, but also has many ancient, endemic plants, as well as species introduced from foreign countries. Among the 30,000 species of plants in China, 18,000 can be found in Yunnan. Yunnan is also home to a variety of animal species, most notably the southeast Asian gaur, a giant forest-dwelling ox, the tiger, and the Asian Elephant. Some already disappeared and are most likely extinct, like the Yunnan Box Turtle and the Yunnan Lar Gibbon.
A main source of wealth lies in its vast mineral resources and mining is the leading industry in Yunnan.. Yunnan has proven deposits of 86 kinds of minerals in 2,700 places. Some 13% of the proved deposits of minerals are the largest of their kind in China, and two-thirds of the deposits are among the largest of their kind in the Yangtze River valley and in south China. Yunnan ranks first in the country in deposits of zinc, lead, tin, cadmium, indium, thallium, and crocidolite. Other deposits include iron, coal, copper, gold, mercury, silver, antimony, and sulfur. More than 150 kinds of minerals have been discovered in the province. The potential value of the proven deposits in Yunnan is 3 trillion yuan, 40% of which come from fuel minerals, 7.3% from metallic minerals, and 52.7% from nonmetallic minerals.
Yunnan has sufficient rainfall and many rivers and lakes. The annual water flow originating in the province is 200 cubic kilometers, three times that of the Yellow River. The rivers flowing into the province from outside add 160 cubic kilometers, which means there are more than ten thousand cubic meters of water for each person in the province. This is four times the average in the country. The rich water resources offer abundant hydro-energy. China is constructing a series of dams on the Mekong to develop it as a waterway and source of power; the first was completed at Manwan in 1993.
Governance
Administrative divisions
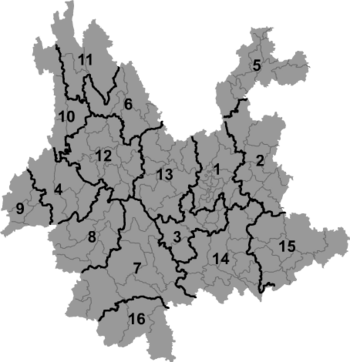
Yunnan consists of sixteen prefecture-level divisions:
| Map | # | Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Administrative Seat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||
| — Prefecture-level city — | |||||
| 1 | Kunming | 昆明市 | Kūnmíng Shì | Panlong District | |
| 2 | Qujing | 曲靖市 | Qǔjìng Shì | Qilin District | |
| 3 | Yuxi | 玉溪市 | Yùxī Shì | Hongta District | |
| 4 | Baoshan | 保山市 | Bǎoshān Shì | Longyang District | |
| 5 | Zhaotong | 昭通市 | Zhāotōng Shì | Zhaoyang District | |
| 6 | Lijiang | 丽江市 | Lìjiāng Shì | Gucheng District | |
| 7 | Pu'er | 普洱市 | Qǔjìng Shì | Simao District | |
| 8 | Lincang | 临沧市 | Líncāng Shì | Linxiang District | |
| — Autonomous prefecture — | |||||
| 9 | Dehong (Dai & Jingpo) | 德宏傣族景颇族自治州 | Déhóng Dǎizú Jǐngpōzú Zìzhìzhōu | Luxi | |
| 10 | Nujiang (Lisu) | 怒江傈僳族自治州 | Nùjiāng Lìsùzú Zìzhìzhōu | Lushui County | |
| 11 | Diqing (Tibetan) | 迪庆藏族自治州 | Díqìng Zàngzú Zìzhìzhōu | Shangri-La County | |
| 12 | Dali (Bai) | 大理白族自治州 | Dàlǐ Báizú Zìzhìzhōu | Dali City | |
| 13 | Chuxiong (Yi) | 楚雄彝族自治州 | Chǔxióng Yízú Zìzhìzhōu | Chuxiong City | |
| 14 | Honghe (Hani & Yi) | 红河哈尼族彝族自治州 | Hónghé Hānízú Yízú Zìzhìzhōu | Mengzi County | |
| 15 | Wenshan (Zhuang & Miao) | 文山壮族苗族自治州 | Wénshān Zhuàngzú Miáozú Zìzhìzhōu | Wenshan County | |
| 16 | Xishuangbanna (Dai) | 西双版纳傣族自治州 | Xīshuāngbǎnnà Dǎizú Zìzhìzhōu | Jinghong City | |
Of those 16 prefecture-level divisions, Yunnan has 129 county-level divisions, and 1455 township-level divisions.
Politics
Secretaries of the CPC Yunnan Committee: The Secretary of the CPC is the highest ranking and most important position in Yunnan.[7]
- Song Renqiong (宋任穷): 1950–1952
- Xie Fuzhi (谢富治): July 1952-August 1959
- Yan Hongyan (阎红彦): August 1959-January 1967
- Zhou Xing (周兴): June 1971-October 1975
- Jia Qiyun (贾启允): October 1975-February 1977
- An Pingsheng (安平生): February 1977-July 1985
- Pu Chaozhu (普朝柱): July 1985-June 1995
- Gao Yan (高严): June 1995-August 1997
- Linghu An (令狐安): August 1997-October 2001
- Bai Enpei (白恩培): October 2001 – incumbent [7]
Governors of Yunnan: The Governor is the second highest office in Yunnan, after the Secretary of the CPC Yunnan Committee.[7] The Governor, who is elected by the Yunnan Provincial People's Congress, is responsible for all economic, environmental, political, personnel and foreign affairs issues concerning Yunnan.[7]
- Chen Geng (陈赓): March 1950-February 1955
- Guo Yingqiu (郭影秋): February 1955-November 1958
- Ding Yichuan (丁一川): November 1958-January 1965
- Zhou Xing (周兴): January 1965–1966
- Tan Furen (谭甫仁): August 1968-October 1970
- Zhou Xing: October 1970-October 1975
- Jia Qiyun (贾启允): October 1975-February 1977
- An Pingsheng (安平生): February 1977-December 1979
- Liu Minghui (刘明辉): December 1979-April 1983
- Pu Chaozhu (普朝柱): April 1983-August 1985
- He Zhiqiang (和志强): August 1985-January 1998
- Li Jiating (李嘉廷): January 1998-June 2001
- Xu Rongkai (徐荣凯): June 2001 – November 2006
- Qin Guangrong (秦光荣): January 2007 [7] -incumbent
Demographics
Ethnicity


Yunnan is noted for a very high level of ethnic diversity. It has the highest number of ethnic groups among all provinces and autonomous regions in China. Among the country's fifty-six recognised ethnic groups, twenty-five are found in Yunnan. Some 38% of the province's population are members of minorities, including the Yi, Bai, Hani, Tai, Dai, Miao, Lisu, Hui, Lahu, Va, Nakhi, Yao, Tibetan, Jingpo, Blang, Pumi, Nu, Achang, Jinuo, Mongolian, Derung, Manchu, Shui, and Buyei. Several other groups are represented, but they live neither in compact settlements nor do they reach the required threshold of five thousand to be awarded the official status of being present in the province. Some groups, such as the Mosuo, who are officially recognised as part of the Naxi, have in the past claimed official status as a national minority, and are now recognised with the status of Mosuo people.
Ethnic groups are widely distributed in the province. Some twenty-five minorities live in compact communities, each of which has a population of more than five thousand. Ten ethnic minorities living in border areas and river valleys include the Hui, Manchu (the Manchu, remnants of the Qing administration, do not live in compact settlements and are in all respects indistinguishable from the Han), Bai, Naxi, Mongolian, Zhuang, Dai, Achang, Buyei and Shui, with a combined population of 4.5 million; those in low mountainous areas are the Hani, Yao, Lahu, Va, Jingpo, Blang and Jino, with a combined population of 5 million; and those in high mountainous areas are Miao, Lisu, Tibetan, Pumi and Drung, with a total population of four million.
An oft-repeated proverb tells the story of three brothers who were born speaking different languages: Tibetan, Naxi, and Bai. Each settled in different areas of Yunnan and Tibet, respectively, the high area, the middle area, and the low area.
Languages
Most dialects of the Chinese language spoken in Yunnan belong to the southwestern subdivision of the Mandarin group, and are therefore very similar to the dialects of neighbouring Sichuan and Guizhou provinces. Notable features found in many Yunnan dialects include the partial or complete loss of distinction between finals /n/ and /ŋ/, as well as the lack of /y/. In addition to the local dialects, most people also speak Standard Chinese (Putonghua, commonly called "Mandarin"), which is used in the media, by the government, and as the language of instruction in education.
Yunnan's ethnic diversity is reflected in its linguistic diversity. Languages spoken in Yunnan include Tibeto-Burman languages such as Bai, Yi, Tibetan, Hani, Jingpo, Lisu, Lahu, Naxi; Tai languages like Zhuang, Bouyei, Dong, Shui, Tai Lü and Tai Nüa or northern Lao dialect; as well as Hmong-Mien languages.
The Naxi, in particular, use the Dongba script, which is the only pictographic writing system in use in the world today. The Dongba script was mainly used to provide the Dongba priests with instructions on how to carry out their rituals: today the Dongba script features more as a tourist attraction. The most famous Western Dongba scholar was Joseph Rock.
Literacy
By the end of 1998, among the province's population, 419,800 had received college education or above, 2.11 million, senior middle school education, 8.3 million, junior middle school education, 18.25 million, primary school education, and 8.25 million aged 15 or above, illiterate or semi-literate.
Agriculture


The region maintains a strong agricultural focus. Agriculture is restricted to the few upland plains, open valleys, and terraced hillsides. Level land for agriculture is extremely scarce and only about 5 percent of the province is under cultivation. Rice is the main crop; corn, barley, wheat, rapeseed, sweet potatoes, soybeans (as a food crop), tea, sugarcane, tobacco, and cotton are also grown. On the steep slopes in the west livestock is raised and timber, a valuable resource, is cut (teak in the southwest).
Tobacco is the main (export) product and makes up a big part of the provincial GDP. Furthermore, Yunnan has a strong competitive potential in the fruit and vegetable industries, especially in low value-added commodities such as fresh and dried vegetables and fresh apples.
Yunnan is one of the regions in the world with the most abundant resources of wild edible mushrooms. In China, there are 938 kinds of edible mushrooms, and over 800 varieties can be found in Yunnan. In 2004, around 7,744 tons of wild edible mushrooms were exported, making up for 70% of the total export of this product in China. The so-called 'pine mushroom' is the main product in Yunnan and is exported to Japan in large quantities.
Another interesting industry with a clear growth potential is the coffee sector. Yunnan is currently China's most important producer of Arabica coffee. Besides the export of roasted coffee, coffee-related products such as extracts, essences and substitutes may be promising products. Yunnan is the birthplace of tea. Still, ancient tea trees can be found in Yunnan of which tealeaves are processed. Tea is becoming an important export product. Especially in the US and Japan the demand is growing.
Due to China's growing consumption of dairy products (a trend heavily supported by the national government), Yunnan's dairy industry is also developing more rapidly and receiving large subsidies from the government develop a competitive edge in Southwest China, but is also aiming to export to its ASEAN neighbors.
Then last but not least, a growing sector, heavily supported by the local government is the horticultural sector. The flower industry in Yunnan province started to develop towards the end of the 1980s. Currently, Yunnan is the most important province nationwide in the field of flower growing. Yunnan province accounts for 50% of China's total cut flower production. The size of the planting area for cut flowers in Yunnan province amounts to 4000 hectares. In 2003, the output totaled 2.3 billion stems. In 2002 the flower industry in Yunnan had a total output of RMB 3.4 billion. Export amounted to USD 18 million. Apart from sales on the domestic market, Yunnan also exports to a number of foreign countries and regions such as Japan, Korea, Hong Kong, Thailand and Singapore.
The rapid developments in this field soon attracted the attention of Dutch horticultural companies and Dutch investments in flower related projects and businesses are steadily growing.
Economy

Yunnan is one of China's relatively undeveloped provinces with more poverty-stricken counties than the other provinces. In 1994, about 7 million people lived below the poverty line of less than an annual average income of 300 yuan per capita. They were distributed in the province's 73 counties mainly and financially supported by the central government. With an input of 3.15 billion yuan in 2002, the absolutely poor rural population in the province has been reduced from 4.05 million in 2000 to 2.86 million. The poverty alleviation plan includes five large projects aimed at improving infrastructure facilities. They involve planned attempts at soil improvement, water conservation, electric power, roads, and "green belt" building. Upon the completion of the projects, the province hopes this will alleviate the shortages of grain, water, electric power and roads.
Yunnan lags behind the east coast of China in relation to socio-economic development. However, because of its geographic location the province has comparative advantages in regional and border trade with countries in southeast Asia. The Lancang River (upper reaches of Mekong River) is the waterway to southeast Asia. In recent years land transportation has been improved to strengthen economic and trade co-operation among countries in the Greater Mekong Subregion. Yunnan's abundance in resources determines that the province's pillar industries are: agriculture, tobacco, mining, hydro-electric power, and tourism. In general, the province still depends on the natural resources. Secondary industry is currently the largest industrial tier in Yunnan, contributing more than 45 percent of GDP. Tertiary industry contributes 40 percent and agriculture 15 percent. Investment is the key driver of Yunnan's economic growth, especially in construction.
The main challenge that Yunnan faces is its lack of major development. Its low productivity and competitiveness restrict the rapid development of the province. The province also faces great challenges in social issues such as environmental protection, poverty elimination, illegal migration, drug trafficking and HIV/AIDS.
Yunnan's four pillar industries include tobacco, agriculture/biology, mining, and tourism. The main manufacturing industries are iron and steel production and copper-smelting, commercial vehicles, chemicals, fertilizers, textiles, and optical instruments. Yunnan has trade contacts with more than seventy countries and regions in the world. Yunnan established the Muse border trade zone (located in Ruili) along its border with Myanmar.[8] Yunnan mainly exports tobacco, machinery and electrical equipment, chemical and agricultural products, and non-ferrous metals. In 2008, its total two-way trade (imports and exports) reached US$9.6 billion. The province signed foreign direct investment contracts involving US$1.69 billion, of which US$777 million were actually utilized during the year. Yunnan's unemployment rate at the end of 2008 was 4.21%.
Yunnan's nominal GDP in 2008 was 570 billion yuan (US$83 billion), an annual growth rate of 11%. Its per capita GDP was 12,587 yuan (US$1,842). The share of GDP of Yunnan's primary, secondary, and tertiary industries were 17.9%, 43%, and 39.1% respectively.
Yunnan is one of the major production bases of copper, lead, zinc, tin and aluminum in China. Gejiu city is well known as "the Kingdom of Zinc" with the reserves ranked first in the country. The Yunxi brand refined tin is one of the main products in Gejiu, which is registered on the London Metal Exchange (LME). Besides, reserves of germanium, indium, zirconium, platinum, rock salt, sylvite, nickel, phosphate, mirabilite, arsenic and blue asbestos are also high. Significant copper deposits are found at Dongchuan, iron ore at Wuding, and coal at Xuanwei and Kaiyuan. Economic policy to locate new industry in interior areas with substantial mineral wealth, led to major industrial development in Yunnan, especially in the Kunming area.
The electricity industry is another important economic pillar of Yunnan, which plays a key role in the "West-East Electricity Transmission Project". The electricity produced in Yunnan is mainly transported to Guangdong Province.
Economic and Technological Development Zones
- Kunming Economic and Technological Development Zone
First established in 1992, Kunming Economic & Technology Development Zone is a national-level zone approved by State Council. Kunming is located in east-central Yunnan province with preferential location. After several years' development, the zone has formed its pillar industries, which include tobacco processing, machinery manufacturing, electronic information, and biotechnology.[9]
- Kunming New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
The Kunming High-tech Industrial Development Zone (KMHNZ), is a state-level high-tech industrial zone established in 1992 in Northwest Kunming, Yunnan Province, China. It is administratively under Kunming Prefecture. It has covers an area of 9 square kilometers. KMHNZ is located in the northwest part of Kunming city, with 4 kilometers from Kunming Railway Station, 5 kilometers from Kunming International Airport.[10]
- Kunming Dianchi Tourism & Vacation Zone
- Kunming Airport Economic Zone
- Ruili Border Trade Economic Cooperation Zone
Ruili Border Economic Cooperation Zone (RLBECZ) is a Chinese State Council-approved Industrial Park based in Ruili City, Dehong Prefecture, Yunnan, China, founded in 1992 and was established to promote trade between China and Myanmar. The area's import and export trade include the processing industry, local agriculture and biological resources are very promising. Sino-Myanmar business is growing fast. Myanmar is now one of Yunnan's biggest foreign trade partners. In 1999, Sino-Myanmar trade accounted for 77.4% of Yunnan's foreign trade. In the same year, exports for electromechanical equipments came up to USD 55.28 million. Main exports here include fiber cloth, cotton yarn, ceresin wax, mechanical equipments, fruits, rice seeds, fiber yarn and tobacco.[11]
- Wanding Border Economic Cooperation Zone
Wanding Border Economic Cooperation Zone (WTBECZ) is a Chinese State Council-approved Industrial Park based in Wanding Town, Ruili City, Dehong Prefecture, Yunnan, China, founded in 1992 and was established to promote trade between China and Myanmar. The zone spans 6 km sq. and is focuses on developing trading, processing, agriculture resources and tourism.[12]
- Qujing Economic and Technological Development Zone
Qujing Economic and Technological Development Zone (QETDZ) is a provincial development zone approved by Yunnan Provincial Government in August 1992. It is located in the east of urban Qujing, the second largest city in Yunnan in terms of economic strengths. The location of the development zone is the economic, political and cultural center of Qujing. As an agency under Qujing municipal Party committee and municipal government, the administrative commission of QETDZ functions as an economy supervising body at the prefecture level and an administration body at the county level. It has 106 km2 under its jurisdiction. It shoulders the task of building a new 40-square-kilometer city area and providing service for a population of 400,000 in the upcoming 10 years.[13]
- Yuxi Economic and Technological Development Zone
- Dali Economic and Technological Development Zone
- Chuxiong Economic and Technological Development Zone
Chuxiong Economic Development Zone is an important zone in Yunnan. Now the zone has attracted a number of investment projects. It is an important industry for the development of new-type industry platform. The zone covers an area of 12 sqkm, composed of four parks.[14]
- Songming Yanglin Experimental Zone for County & Township Industries
- Hekou Border Economic Cooperation Zone
First established in 1992, Hekou Border Economic Cooperation Zone is a border zone approved by State Council in China to promote trade between China and Vietnam. It has a planned area of 4.02 square kilometers. The zone implemented several policies to serve its clients in China from various industries and sectors including investment, trade, finance, taxation, immigration and etc.[15]
- Jiegao Border Trade Economic Zone
- Lijiang Yulong Snow Mountain Tourism Zone
- Cangshan Mountain & Erhai Lake Tourism and Vacation Zone at Dali
- Xishuangbanna Tourism and Vacation Zone
- Tengchong Tourism and Vacation Zone
- Yangzonghai Lake Tourism and Vacation Zone
- Fuxian Lake Tourism and Vacation Zone
Education
Since the 1960s, improvements have been achieved in the overall educational level, which can be seen in the increase in average years of regular education received. The development of part-time schools have brought adult, distance and continuing education to farms, factories, offices, and other places. Evening, time off work / study leave classes allow people to receive education without leaving their jobs. Policies to upgrade adult education have begun to complement the campaign against illiteracy. A basic Chinese vocabulary in simplified strokes is taught to millions of illiterate people in short, intensive courses. Despite progress made, Yunnan's illiteracy rate remains one of the highest in China mainly due to insufficient education among minority peoples.[16][17]
In higher education, Yunnan has one "National Key University"—Yunnan University in Kunming. There is also a growing number of technical schools, among which the most prominent are the Southwest Forestry University, Yunnan Agricultural University, Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Kunming Medical University, Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and Kunming University of Science and Technology. Other notable establishments of learning are the , the Yunnan Astronomical Observatory, and the Yunnan Provincial Library.As of 2000, there were 24 institutions of higher learning in Yunnan, with an enrollment of over 90,400 students and a faculty of 9,237; 2,562 secondary schools with an enrollment of more than 2,137,400 students and 120,461 teachers; and 22,151 primary schools with an enrollment of 4,720,600 pupils and a faculty of 210,507. The gross enrollment rate of school-age children was 99.02%.
See also: List of universities and colleges in Yunnan
Health
Yunnan Province is responsible for about 50% of officially reported malaria cases in China.[18]
It is presently considered to be the main source of plague in China.[19]
HIV-AIDS
- HIV/AIDS in Yunnan
Transportation

Railways
Yunnan was first connected by railway not to the rest of China, but to the Vietnamese port of Haiphong by a French engineered narrow gauge railway, the Sino-Vietnamese Railway completed in 1910. It took another fifty years for the province to be connected by rail to the rest of China with the completion of the Chengdu–Kunming line. Later a line connecting Kunming to Guiyang followed. Two further lines have been added recently: a southern line connecting to Nanning and a north-eastern line connecting to Sichuan via Yibin.
An extension now also links Kunming to Dali, with the stretch to Lijiang nearing completion. Plans are underway on extending the old line to Vietnam, while a new and very ambitious plan to link from Dali to Ruili has been announced in 2006. Another plan to extend the railway line from Kunming all the way to Singapore, with connections to the other South East Asian countries, will be opened in 2017.
Road and railroad traffic has been recently improved, and Kunming is now a transportation center; an important railroad runs from Kunming to Hanoi, Vietnam, while transportation to Myanmar is maintained by the Burma Road.
Burma Road
The Burma Road was a highway extending about 1,126 km (700 mi) through mountainous terrain from Lashio, northeast Burma northeastward to Kunming, China. Undertaken by the Chinese after the start of the Sino-Japanese War in 1937 and completed in 1938, it was a vital transportation route for wartime supplies to the Chinese government from Rangoon and shipped by railroad to Lashio from 1938 to 1946. An extension runs east through China from Kunming, then north to Chongqing. This traffic increased in importance to China after the Japanese took effective control of the Chinese coast and of Indochina. It was seized by the Japanese in 1942 and reopened when it was connected to the Stilwell Road from India. The Ledo Road (later called the Stilwell Road) from Ledo, India, into Myanmar was begun in December 1942. In 1944 the Ledo Road reached Myitkyina and was joined to the Burma Road. Both roads have lost their former importance and are in a state of disrepair. The Burma Road's importance diminished after World War II, but it has remained a link in a 3,400-km road system from Yangon, Myanmar, to Chongqing.
Highways
Road construction in Yunnan continues unabated: over the last years the province has added more new roads than any other province. Today expressways link Kunming through Dali to Baoshan, Kunming to Mojiang (on the way to Jinghong), Kunming to Qujing, Kunming to Shilin (Stone Forest). The official plan is to connect all major towns and neighbouring capitals with expressways by 2010, and to complete a high-speed road network by 2020.
All county towns are now accessible by paved, all-weather roads from Kunming, all townships have a road connection (the last to be connected was Yangla, in the far north, but Dulongjiang remains cut off for about six months every year), and about half of all villages have road access.
Second-level national highways stretch 958 km, third-level highways, 7,571 km and fourth-level highways, 52,248 km. The province has formed a network of communication lines radiating from Kunming to Sichuan and Guizhou provinces and Guangxi and Tibet autonomous regions, and further on to Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam and Thailand.
National highways running through Yunnan province are:
- China National Highway 108
- China National Highway 213
- China National Highway 214
- China National Highway 320
- China National Highway 323
- China National Highway 324
- China National Highway 326
Luofu Expressway
After the opening of the Suolongsi to Pingyuanjie expressway, Luofu expressway, the first between Yunnan and Guangxi Province, opened on October 2007. It has made material and passenger transportation between the two provinces much more convenient. Moreover, Luofu Expressway has also become the main road from Yunnan to Guangxi and the coastal ports. Luofu Expressway begins from the crossroads of Luo Village between Yunnan and Guangxi Provinces and ends at Funing County of Wenshan State. The total length of the expressway is 79.3 kilometers which has shortened the commute between Yunnan and Guangxi from the previous 3 and half hours to just 50 minutes.
Expressways running through Yunnan province are:
- Kunming–Bangkok Expressway
- G5611 Dali Expressway from Dali to Lijiang
- G78 Shankun Expressway from Shantou to Kunming
- G80 Guangkun Expressway from Guangzhou to Kunming
- G8011 Kaihe Expressway from Kaiyuan to Hekou on the Vietnamese border
Waterways
Generally, rivers are obstacles to transport in Yunnan. Only very small parts of Yunnan's river systems are navigable. However, China is constructing a series of dams on the Mekong to develop it as a waterway and source of power; the first was completed at Manwan in 1993.
In 1995, the province put an investment of 171 million yuan to add another 807 km of navigation lines. It built two wharfs with an annual handling capacity of 300,000 to 400,000 tons each and four wharfs with an annual handling capacity of 100,000 tons each. The annual volume of goods transported was two million tons and that of passengers transported, two million.
Airports
The province has twenty domestic air routes from Kunming to Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Chengdu, Haikou, Chongqing, Shenyang, Harbin, Wuhan, Xi'an, Lanzhou, Hangzhou, Xiamen, Nanning, Shenzhen, Guiyang, Changsha, Guilin, Lhasa and Hong Kong; ten provincial air routes from Kunming to Jinghong, Mangshi, Lincang, Tengchong, Lijiang, Dali, Zhongdian (Shangri-la), Zhaotong, Baoshan and Simao; and ten international air routes from Kunming to Bangkok, Calcutta, Chiang Mai, Yangon, Singapore, Seoul, Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, Kuala Lumpur and Vientiane.
The Wujiaba Airport in Kunming is a national first-class airport and the other airports are second-class terminals. A new airport for Kunming, to be built east of the city at Dabanqiao, began construction in 2006, but is not expected to be completed until 2015.
Culture

Yunnan's cultural life is one of remarkable diversity. Archaeological findings have unearthed sacred burial structures holding elegant bronzes in Jinning, south of Kunming. In Zhaotong in northeastern Yunnan, there has been discovered, frescos of the Jin Dynasty (265–420). Many Chinese cultural relics have been discovered in later periods. The lineage of tribal way of life of the indigenous peoples persisted uninfluenced by modernity until the mid-20th century. Tribal traditions, such as Yi slaveholding and Wa headhunting, have since been abolished. After the Cultural Revolution (1966–76), when many minority culture and religious practices were suppressed, Yunnan has come to celebrate its cultural diversity and subsequently many local customs and festivals have flourished.[20]
Eighteen Oddities of Yunnan
Cuisine
Tea
One of Yunnan's famous products is Pu-erh tea, named after the old tea trading town of Pu-erh. The province is also known for its Yunnan Gold and other Dianhong teas, developed in the 20th century.
Music
Chinese medicine
Yunnan is host to 15,000 species of plants, including 60 percent of the plants used in traditional Chinese medicine.
- Yunnan Baiyao
Tourism
Yunnan Province, due to its beautiful landscapes, mild climate and colorful ethnic minorities, is one of China's major tourist destinations. Most visitors are Chinese tourists, although trips to Yunnan are organized by an increasing number of foreign travel agencies as well. Mainland tourists travel by the masses; 2.75 million Chinese visited Yunnan last October during National Holiday. Also a different trend is slowly developing; small scale and environmentally friendly ecotourism. At the moment projects in this field are often being set up with help of NGO's.
In 2004, tourism revenues amounted to 37 billion RMB, and thus accounting for 12, 6% of the provincial GDP. Another fact indicating the importance of tourism in Yunnan Province is capital Kunming hosting the China International Travel Mart every two years. This tourism trade fair is the largest of its kind in Asia and serves as an important platform for professionals in the sector. More than 80 countries and regions were present during the 2005 edition.
Tourist centres in Yunnan include:
- Dali, the historic center of the Nanzhao and Dali kingdoms.
- Chuxiong, the first stop on the way to Dali and Lijiang. Home of the Yi ethnic minority and their respective ancient town.
- Jinghong, the center and prefectural capital of the Xishuangbanna Dai minority autonomous prefecture.
- Lijiang, a Naxi minority city. It has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1997.
- Shangri-La County (formerly Zhongdian), an ethnic Tibetan township and county set high in Yunnan's north-western mountains.
- Shilin (Stone Forest), a series of karst outcrops east of Kunming.
- Yuanyang, a Hani minority settlement with vast rice-terraces.
- Xishuangbanna, a national scenic resort, famous for its natural and cultural attractions.
Places of interest
- Black Dragon Pool
- Baishutai
- Cangshan
- Erhai Lake
- Ganlan Basin
- Green Lake Park
- Jade Dragon Snow Mountain
- Lancang River (Mekong River)
- Manting Park (Chunhuan Park) in Jinghong
- Meili Snow Mountain in Deqin
- Pujian Temple
- Sanchahe Nature Reserve in Jinghong
- ShaPing Market, Dali
- Shaxi
- Stone Forest
- Three Pagodas
- Tengchong (hot springs)
- Tiger Leaping Gorge
- Visitor Center for Nature and Culture in Northwest Yunnan
- Wase markets, near Dali
- Xishuangbanna Tropical Flower & Plant Garden
- Yuantong Temple
- Yunnan Provincial Museum
Sport
Professional sporting teams in Yunnan include, Yunnan Bulls in the Chinese Basketball Association. Football teams include Yunnan Lijiang Dongba and the defunct Yunnan Hongta.
See also
- Greater Mekong Subregion
- 1996 Lijiang earthquake
- Yunnan Institute of Development
- List of prisons in Yunnan province
References
- ↑ (Chinese) Origin of the Names of China's Provinces, People's Daily Online.
- ↑ John Man-Kublai Khan, p.80
- ↑ An Australian in China
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ http://www.kunming.org.cn/index/content/2009-01/09/content_1700783.htm
- ↑ http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1248
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 "Qin Guangrong re-elected governor of Yunnan Province". Xinhua. 2008-01-24. http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2008-01/24/content_7490786.htm. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- ↑ "Myanmar to open second largest border trade zone". People's Daily Online. February 13, 2006. http://english.people.com.cn/200602/13/eng20060213_242330.html. Retrieved 2008-10-14.
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Kunming Economic & Technology Development Zone
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Kunming High-tech Industrial Development Zone
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Ruili Border Economic Cooperation Zone
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Qujing Economic and Technological Development Zone
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Chuxiong Economic Development Zone
- ↑ RightSite.asia | Hekou Border Economic Cooperation Zone
- ↑ L. Tian, J. Li, K. Zhang, P. Guest. "Women's status, institutional barriers and reproductive health care: A case study in Yunnan, China". Health Policy, Volume 84, Issue 2, Pages 284–297
- ↑ Literacy Co-ordination Office of Yunnan Province
- ↑ Yunnan DQ Testing Turns Up Fake Artesunates, Health Officials Alerted USP Drug Quality and Information Program
- ↑ Zhang Z, Hai R, Song Z, Xia L, Liang Y, Cai H, Liang Y, Shen X, Zhang E, Xu J, Yu D, Yu XJ. (2009) Spatial variation of Yersinia pestis from Yunnan Province of China. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 81(4):714-717
- ↑ http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/BKK83023.htm
Further reading
- Books
- Stephen Mansfield (2007) China: Yunnan Province. (Bradt Travel Guide China: Yunnan Province) ISBN 1-84162-169-2
- Ann Helen Unger and Walter Unger. (2007) Yunnan: China's Most Beautiful Province. (Orchid Press) ISBN 3-7774-8390-7
- Damien Harper. (2007) China's Southwest. (Lonely Planet Country & Regional Guides) ISBN 1-74104-185-6
- Patrick R. Booz. (1998) Yunnan. (Odyssey Passport: McGraw-Hill Contemporary) ISBN 0-8442-9664-3
- Susan K. McCarthy. (2009) Communist Multiculturalism: Ethnic Revival in Southwest China (University of Washington Press) ISBN 0-295-98909-2
- Web
- Population Profile of Yunnan – United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
- Economic Profile of Yunnan – Hong Kong Trade Development Council
- Economic Integration of Yunnan with the Greater Mekong Subregion Asian Economic Journal Volume 20 Issue 3, Pages 303–317
External links
- Yunnan Province e-Government website
- Yunnan Provincial Department of Commerce
- Yunnan Environmental Development Program
- Yunnan Nature Conservation
- Yunnan Daily and Yunnan Info Daily newspapers
- Yunnan Astronomical Observatory (YNAO)
- Yunnan at Google Maps
- Yunnan Tourism Information Network (official)
- Yunnan travel guide from Wikitravel
- Yunnan at Open Directory Project
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
